Guide: How to Add Coin or Token to Trust Wallet

In this article we are going to guide you with step by step procedure of adding, editing tokens to your Trustwallet
How to Add a Custom Token to Trustwallet?
We are here to help you with adding KRRX token to your Trust Wallet app. KRRX is a native token of a quite-known crypto trading platform - Kyrrex. So, what’s the reason for investors and traders adding the token to Trust Wallet? It provides many features to its holders like decreasing trading commissions, stacking, and the possibility to catch the token’s growth from the beginning.
Kyrrex is a crypto exchange company regulated by Malta and Estonia authorities. So, investing in its native token can be a profitable bet even during a short period of time. As we can see, KRRX provides many outstanding possibilities. Trust Wallet supports many blockchains and over one thousand crypto tokens. The system keeps providing us with brand new chains/tokens every week.
By default, Trust Wallet allows us to work with Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and Binance (BNB). So, what should you do if you need an extra token in your crypto wallet?
There are several simple steps to do it.
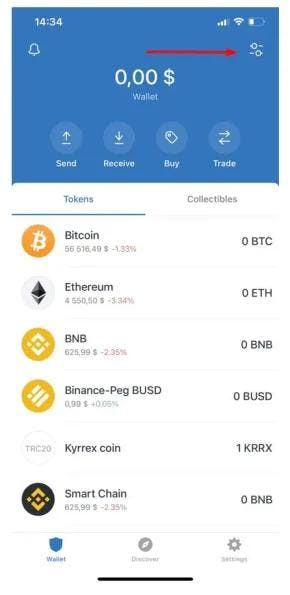
Step 1: Click on the manage button
The manage button is located in upper right corner of your Trust wallet app. Clicking on it will give you access to the app's Menu.
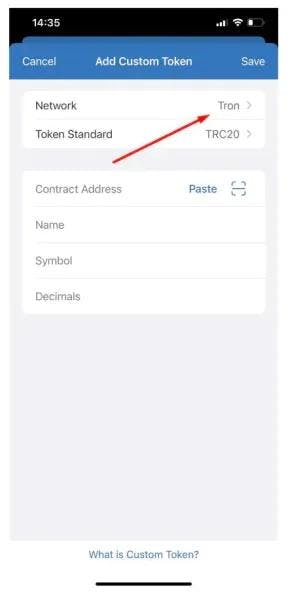
Step 2: Adding Custom Token
When you are on the Manage page, please, scroll down the list. You have to click an “Add Custom Token” button to add an extra coin to the list.

Step 3: Choosing Tron network
We have to be sure that the support network is Tron (TRC20). If it’s already Tron, no changes needed.
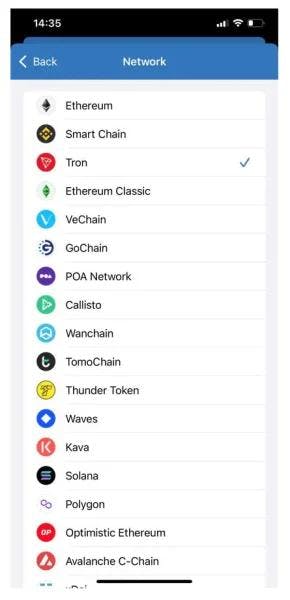
If not, pick the Tron network from the list.
Step 4: fill out the contract address
You have to fill out the contract address:
THS2ZuQowumzFPD1z3wchB1PijWMggUgmA
The rest of the data like Name, Symbol, and Decimals will be autofilled. If not, we have to fill them manually than click Save.
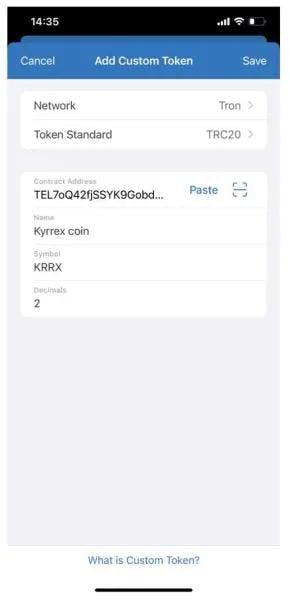
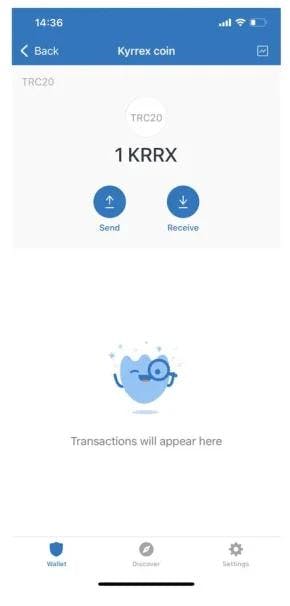
Step 5: Completion
Now, you’re good! Everything is set just right. If not, please, contact the technical support. As we can see, adding a custom token in the Trust Wallet is simple.
So, you are set to invest in the KRRX tokens and catch shining profits with Kyrrex.
About Kyrrex
Kyrrex is a multifunctional professional platform for trading and storing cryptocurrencies
Tags
Categories
Related articles

Tokenomics 101: Explaining the Basics and Beyond of Token Economy
Tokenomics, a fusion of 'token' and 'economics,' refers to the economic principles and models underpinning digital currencies within the blockchain sphere. This intricate ecosystem encompasses various factors such as token supply, demand, distribution methods, and overall market valuation, playing a pivotal role in the sustainability and success of cryptocurrency projects. Unlike traditional economies, governed by centralized financial systems and regulatory bodies, tokenomics operates within a decentralized framework, offering innovative approaches to value creation, transfer, and management.
As the digital asset landscape continues to expand, understanding the fundamentals of token economy becomes crucial for investors, developers, and enthusiasts alike. This article aims to demystify tokenomics, guiding you through its core components, real-world applications, and the impact on the broader crypto economy.
Tokenomics and token economy
Tokenomics represents the study and structural framework of a token's economy within the blockchain sphere, encompassing aspects like supply, demand, distribution, and valuation. In this system, the token economy operates under a unique set of rules and mechanisms distinct from traditional economies. Supply refers to the total quantity of tokens available, which can be fixed like Bitcoin's 21 million cap, or variable as seen in some governance token models. Demand is influenced by the token's utility, perceived value, and market conditions.
Distribution entails how tokens are allocated or issued to users, investors, and the project's team, which can significantly impact the token's initial and ongoing valuation. Valuation, meanwhile, derives from market perceptions, utility, and the token's inherent properties, such as security features or governance rights.
Unlike traditional monetary systems controlled by central authorities, the token economy leverages blockchain technology to enable a decentralized, transparent, and secure environment. Here, market dynamics are not influenced by central bank policies but by code, community consensus, and decentralized protocols. This paradigm shift from centralized to decentralized finance represents a significant evolution in how value and economy are conceptualized and managed within the digital age.
Key Components of Tokenomics
Tokenomics delves deep into the operational and economic facets of tokens within blockchain projects. Understanding these components is critical for grasping how tokens gain and maintain their value.
1- Minting
The process of minting involves creating or generating tokens within a blockchain project. Different protocols have varied methods; Bitcoin, for example, rewards miners for validating transactions, thus "minting" new coins. Ethereum initially distributed Ether through an Initial Coin Offering (ICO), but also mints new Ether as rewards in transaction processing. The method of minting impacts the initial and ongoing supply of tokens, influencing scarcity and value.
2- Utility
Tokens must serve a purpose within their ecosystems; this utility drives demand. Bitcoin's primary utility is as a digital currency, while Ethereum's Ether is used to perform transactions and run applications on its network. Other tokens might grant voting rights in project governance (governance tokens), access to services, or act as a stake in decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms.
3- Supply and Demand
The principles of supply and demand heavily influence token economics. If a token has a capped supply (like Bitcoin), scarcity can increase demand, potentially raising its value. Conversely, if a token's supply is vast or infinite, its value might be lower unless there is significant demand. Market perception, technological advancements, and broader economic factors also play into this dynamic.
4- Distribution and Allocation
The method of token distribution can affect its long-term value and security. Initial allocation might occur through public sales (ICOs or IDOs), community rewards, or allocations to founders and early investors. Projects like Solana and Cardano have allocated significant portions of their tokens to insiders but have maintained public interest through transparency and project utility.
5- Vesting and Inflation
Vesting schedules and inflation control are critical for maintaining a token's value and ensuring project longevity. Vesting prevents market flooding by slowly releasing tokens to developers or investors, maintaining stability. Projects can control inflation through mechanisms like token burning or halving events, as seen with Bitcoin, which undergo periodical "halvings" reducing the reward for mining new blocks, thus controlling the rate of new token introduction into the ecosystem.
Each of these components must be carefully balanced to create a sustainable and successful tokenomics model. Missteps in any area can lead to issues like rapid devaluation, lack of interest, or even project failure.
Examples of Real-World Token economy in Action
Tokenomics comes to life in various blockchain projects, each employing unique strategies to enhance their ecosystem's value and usability.
Ethereum
As a pioneer, Ethereum revolutionized the blockchain space by introducing smart contracts. These are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. Ethereum's token, Ether, serves primarily as a utility token, necessary for conducting transactions and executing contracts on the Ethereum network. Its initial distribution was through an ICO, establishing an initial supply that has since increased due to block rewards. Ethereum's shift from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS) in the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade impacts its tokenomics by changing the reward structure and potentially reducing the rate of new Ether creation, influencing scarcity and value. Transaction fees, known as "gas," also play a crucial role, as they vary based on network demand, adding an economic layer to operation prioritization.
Solana
Known for its incredible speed and lower transaction costs, Solana has emerged as a highly efficient blockchain platform. Solana's native token, SOL, is used to pay for transactions and for staking as part of its Proof of History (PoH) and Proof of Stake (PoS) hybrid consensus mechanism. The initial supply was determined at its launch, with ongoing emissions governed by inflationary policies aimed at incentivizing validators and stakers. Solana has a deflationary aspect as well, where transaction fees are burned, reducing the total supply and potentially increasing the value of remaining SOL tokens over time.
Cardano
Cardano differentiates itself through a strong emphasis on peer-reviewed academic research and formal methods in its development process, ensuring a high degree of security and scalability. ADA, Cardano's native token, is used for transaction fees and staking within its PoS consensus mechanism, Ouroboros. The initial supply was set during its ICO, with a defined maximum supply cap to prevent inflation. Staking ADA not only supports network security and operation but also rewards users, distributing new ADA created through inflation and transaction fees based on their stake. The design aims to balance between rewarding holders and ensuring long-term sustainability, reflecting Cardano's research-driven approach to blockchain development.
Diverse approaches to tokenomics can significantly impact a project's success and the value of its associated tokens. Each project's unique strategy — whether focusing on technological innovation, efficiency, or academic rigor — plays a critical role in shaping its token economy and overall ecosystem.
Impact of Token economy on Investors and Projects
Token economy significantly influences both investor decision-making and the overall success of cryptocurrency projects. Investors scrutinize tokenomics for insights into a project's long-term viability, supply scarcity, and potential return on investment. They assess factors such as token distribution, utility, and inflationary controls to gauge the risk and potential growth of their investments. A project with clear, fair token distribution and a practical utility for its token is more likely to attract and retain investors.
For projects, well-structured tokenomics is crucial for sustainability and achieving set objectives. Proper tokenomics ensures that the project is adequately funded and that incentives are aligned between the developers, users, and investors. It helps maintain a balanced ecosystem where tokens circulate effectively, facilitating transactions, rewarding participants, and funding continued development. The long-term success and adoption of crypto projects heavily depend on their tokenomic models, which should be designed to support growth, stability, and engagement within the ecosystem.
Trends and Challenges in Crypto Token Economy
Trends already influencing token economics include the integration of governance tokens, enhancing decentralized decision-making within projects. These tokens empower holders with voting rights on project developments, potentially increasing user engagement and investment in the project's future. Additionally, the trend towards deflationary token models, where the total supply decreases over time, could create scarcity, driving demand and potentially increasing token value.
Another emerging trend is the use of layer-two solutions and cross-chain interoperability to enhance transaction efficiency and reduce costs, directly impacting the utility and attractiveness of a project's token. However, these advancements come with challenges, including regulatory uncertainty and the need for robust security measures to prevent fraud and ensure user trust.
However, creating a balanced and sustainable token economy remains a complex challenge. Projects must design tokenomics that incentivize participation and growth without leading to over-centralization or excessive inflation. They must navigate these waters while maintaining compliance with an ever-changing global regulatory landscape, which can significantly impact token valuation and project operations.
Conclusion
Tokenomics is essential in assessing a cryptocurrency's potential. A well-designed economic model can lead to a project's success, while a poor one can doom it. For investors and creators alike, a deep understanding of tokenomics is crucial in navigating the burgeoning field of digital currencies.
For more info and trendy articles check our Crypto Blog.

MiCA Unveiled: Guide to Licensing and Compliance for Crypto Companies
In a fragmented regulatory landscape, the Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation emerges as a beacon of standardization and security. The European Union's pioneering approach to crypto regulation, embodied in MiCA, sets a precedent for the global crypto market. MiCA isn't just another regulatory hurdle; it's a transformative framework that promises to bring clarity and confidence to both crypto businesses and investors. As we delve into this comprehensive guide, we'll uncover the intricacies of MiCA, illuminating the path for businesses striving to navigate this new regulatory landscape.
Understanding the Scope of MiCA
The MiCA crypto regulation is tailored to encompass the broad spectrum of crypto-assets, excluding only those classified as financial instruments under existing EU legislation. This inclusivity marks MiCA as a comprehensive framework, addressing a range of assets from stablecoins to utility tokens. The regulation aims to establish uniform rules across all EU member states, effectively eliminating the regulatory patchwork that currently complicates the crypto market.
The heart of MiCA revolves around consumer protection, market integrity, and financial stability. By introducing a standardized set of rules, MiCA crypto regulation ensures a safer environment for investors, shielding them from the market's volatility and the potential risks associated with digital asset investments. For crypto businesses, this translates to a more predictable and secure operating environment.
Licensing Requirements under MiCA
Navigating the licensing landscape under MiCA requires a deep understanding of its requisites. Primarily, any crypto company operating within the EU must be fully licensed and compliant with MiCA standards. This includes a broad spectrum of entities from crypto exchanges to wallet providers.
The licensing process under MiCA is meticulous and requires companies to demonstrate a high level of operational and financial robustness. Key elements include robust IT infrastructure, stringent AML (Anti-Money Laundering) policies, and comprehensive risk management frameworks. These requirements are not just formalities; they are essential to ensuring that companies can withstand the volatile nature of the crypto market and protect their clients' investments.
Here is a breakdown of the requirements and standards for obtaining a MiCA crypto license:
- Submission of Application: Legal entities or other undertakings intending to provide crypto-asset services must submit their application for a MiCA license to the competent authority of their home Member State.
- Application Contents: The application should contain specific information, including proof of the good repute and appropriate knowledge, skills, and experience of the management body, details of shareholders with qualifying holdings, descriptions of internal control mechanisms, ICT systems, procedures for segregation of clients' crypto-assets and funds, and complaints-handling procedures.
- Assessment of Completeness: Competent authorities will assess whether the application is complete within 25 working days of receipt. If the application is not complete, a deadline will be set for the applicant to provide any missing information.
- Notification of Complete Application: Once an application is deemed complete, competent authorities will notify the applicant crypto-asset service provider.
- Assessment of Compliance: Competent authorities will assess the application for compliance with MiCA requirements within 60 working days of receiving a complete application. This assessment may include a review of the crypto-asset white paper and cooperation with anti-money laundering and counter-terrorist financing bodies.
- Draft Decision: A fully reasoned draft decision granting or refusing authorization will be made by the competent authorities based on the assessment.
- Potential Suspension of Assessment: The assessment period may be suspended if the competent authorities request additional information from the applicant. The suspension shall not exceed 20 working days.
- Consultation Before Authorization: Before granting or refusing authorization, competent authorities shall consult relevant bodies or authorities as required.
These steps outline the structured approach to obtaining a MiCA license, focusing on compliance, transparency, and the integrity of the applicant.Top of Form Each step in this process is crucial for obtaining and maintaining a MiCA crypto license. It's important for companies to approach each stage with thorough preparation and a commitment to maintaining high standards of compliance.Top of Form
MiCA's licensing requirements are designed to foster a transparent, fair, and stable crypto market in the EU. For a crypto-fiat bank like Kyrrex, complying with these regulations is a testament to its commitment to providing secure and compliant crypto services. Kyrrex's alignment with MiCA regulations showcases its dedication to maintaining the highest standards of operational integrity and customer protection.
Businesses that Fall Under the MiCA Licensing Requirements
Here's a general list of the types of companies and businesses that the MiCA licensing requirement covers:
- Crypto-Asset Service Providers (CASPs): These include entities operating trading platforms, exchanges (crypto-to-fiat and crypto-to-crypto), and those offering custody or administration services for crypto-assets.
- Issuers of Asset-Referenced Tokens (ARTs): Companies issuing ARTs, which are crypto-assets aiming to stabilize their value by referencing other assets or a combination of assets, including fiat currencies.
- Issuers of E-Money Tokens (EMTs): Entities issuing EMTs, which are designed to maintain stable value by referencing a single fiat currency, similar to electronic money.
- Providers of Crypto-Asset Exchange Services: Companies facilitating the exchange of crypto-assets for fiat currency or other crypto-assets.
- Crypto-Asset Custody and Wallet Providers: Businesses offering secure storage and management of crypto-assets for clients.
- Firms Providing Crypto-Asset Advisory Services: Companies offering advice related to investment in crypto-assets.
- Crypto-Asset Issuers (excluding ARTs and EMTs): Entities responsible for the creation and initial distribution of various types of crypto-assets, excluding asset-referenced and e-money tokens.
Compliance Challenges and Solutions
Compliance with MiCA presents a unique set of challenges for crypto companies. Adapting to a new regulatory environment requires significant changes in operational, legal, and compliance structures. The primary challenge lies in the constant evolution of the crypto market, which demands that companies remain agile and informed.
To overcome these challenges, companies should implement a number of constructive measures, especially the ones outlined below:
- Invest in Compliance Systems: Companies should allocate resources to develop and maintain robust compliance systems that align with MiCA standards.
- Staff Training: Regular training programs for staff to ensure they are up-to-date with MiCA regulations and compliance procedures.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Implement a schedule for regular internal audits to assess and ensure adherence to compliance standards.
- Ongoing Reviews: Conduct periodic reviews of internal processes and policies to align with evolving MiCA regulations.
- Technological Advancements: Utilize advanced technology solutions to streamline and enhance compliance processes.
- Collaboration with Regulators: Engage in ongoing dialogue and collaboration with regulatory bodies for insights and guidance on compliance matters.
- Industry Collaboration: Work alongside other industry players to share best practices and navigate MiCA compliance complexities together.
- Proactive Approach: Adopt a forward-thinking strategy to view compliance not just as a requirement, but as an opportunity for growth and establishing market leadership.
Each of these steps plays a crucial role in ensuring that a company meets the MiCA compliance requirements. By adopting a proactive approach, companies can turn these challenges into opportunities for growth and market leadership.
For Kyrrex, adhering to MiCA standards is part of its broader strategy to ensure the highest level of service quality and security. It reflects the company's dedication to being at the forefront of regulatory compliance, setting a benchmark for other players in the industry.
Preparing for the Future: Next Steps for Crypto Companies
As MiCA paves the way for a regulated crypto market in the EU, companies need to prepare for its implementation. The first step is gaining a thorough understanding of MiCA's provisions and how they impact different aspects of crypto operations.
Crypto companies should start by assessing their current compliance status and identifying areas that need improvement. This may involve restructuring certain business practices, enhancing security measures, and updating internal policies.
It's also crucial for companies to stay updated with ongoing regulatory developments. Engaging with legal and compliance experts can provide valuable insights and ensure that companies remain on the right side of these evolving regulations.
Conclusion
MiCA marks a significant milestone in the journey towards a regulated and secure crypto market. For companies operating in this space, understanding and complying with MiCA is not just about adherence to regulations; it's about embracing a new era of transparency, security, and consumer trust.

How to Transfer Crypto to Bank Account?
Introduction
The digital age has ushered in revolutionary changes, and one of the most significant is the advent of cryptocurrencies. These digital currencies, decentralized and often volatile, have captured the imagination of investors, tech enthusiasts, and everyday consumers alike. As cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others gain mainstream acceptance, an increasing number of people are looking for ways to bridge the gap between the digital currency world and traditional finance. One key aspect of this integration is understanding how to transfer crypto to a bank account effectively and safely.
This process is not as straightforward as a typical bank transfer. It involves understanding the nuances of digital currencies, the role of crypto platforms, and the intricacies of the financial systems that govern these transactions. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the steps necessary to transfer your crypto assets to your bank account, focusing on the use of centralized crypto banks and reliable crypto platforms. Whether you are a seasoned investor or new to the world of digital currencies, this article aims to provide a clear, step-by-step approach to demystify the process and ensure a smooth transfer of your crypto assets to your traditional bank account.
Understanding Cryptocurrency and Bank Transfers
Cryptocurrencies: A Brief Overview
Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual currencies that use cryptography for security and operate on a technology called blockchain, a decentralized technology spread across many computers that manage and record transactions. Part of the appeal of this technology is its security.
The Role of Centralized Crypto Banks
Centralized crypto banks bridge the gap between the traditional financial world and the burgeoning world of cryptocurrencies. They are financial institutions that specialize in dealing with digital currencies, offering services similar to conventional banks but with cryptocurrencies. These banks allow users to store, manage, and transfer their digital assets, providing a crucial link for converting cryptocurrencies into fiat currency, which can then be transferred to a traditional bank account.
Crypto Platforms: The Facilitators
Crypto platforms are online services that enable the buying, selling, and transferring of cryptocurrencies. They play a pivotal role in the crypto banking process. These platforms act as intermediaries, providing the tools and services needed to convert cryptocurrencies into fiat money, and subsequently, transfer it to a bank account. Choosing a reliable and secure crypto platform is crucial for a safe and efficient transfer process.
Step-by-Step Guide to Transferring Crypto to a Bank Account
Transferring cryptocurrency to a traditional bank account involves several steps. Here's a comprehensive guide to navigate this process:
1. Selecting a Reliable Crypto Platform
- Research and Choose Wisely: Begin by researching crypto platforms that offer bank transfer services. Look for platforms known for their security, user-friendly interface, and low transaction fees.
2. Creating and Verifying an Account
- Set Up Your Account: Once you've chosen a platform, create an account. This will typically require providing some personal information and going through a verification process to comply with financial regulations.
3. Transferring Cryptocurrency from Your Wallet to the Platform
- Deposit Your Crypto: Transfer the cryptocurrency from your personal wallet to your account on the platform. This step usually involves generating a deposit address on the platform and sending your crypto to this address.
4. Converting Cryptocurrency to Your Local Currency
- Sell Your Cryptocurrency: Once your crypto is in your platform account, sell it for your local currency. This step is crucial as banks only deal with fiat currencies.
5. Transferring Funds to Your Bank Account
- Withdraw to Bank Account: After selling your crypto for fiat currency, you can withdraw the money to your bank account. Enter your bank details and initiate the transfer. Be aware of any withdrawal limits and processing times.
Each of these steps involves careful consideration, especially in selecting the right platform and understanding the transaction fees and processing times involved.
Choosing the Right Crypto Platform
When it comes to transferring crypto to your bank account, the choice of platform is paramount. Here are key factors to consider:
Safety First: Opt for platforms with robust security measures like two-factor authentication, cold storage for funds, and insurance against theft or hacking.
Cost-Effectiveness: Consider the transaction fees, which can vary widely. Lower fees can make a significant difference, especially for large transfers.
User-Friendly Interface: Choose a platform with an intuitive interface, especially if you are new to crypto transactions.
Centralized Crypto Banks: A Reliable Option
Centralized crypto bank like Kyrrex Crypto Bank offer an amalgamation of traditional banking services and modern cryptocurrency features. They provide a seamless experience for those looking to transfer crypto assets to bank accounts. Such institutions are characterized by:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring your transactions are legally compliant.
- Integrated Services: Offering a one-stop solution for crypto and fiat transactions.
- Customer Support: Providing assistance for any issues during the transfer process.
Choosing the right crypto platform or a centralized crypto bank is crucial for a smooth, secure, and cost-effective transfer of your crypto assets to your bank account.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Transferring cryptocurrency to a bank account can present some challenges. Understanding these and knowing how to address them can make the process smoother and more efficient.
Challenge 1: Transaction Delays
- The Issue: Transfers can sometimes take longer than expected due to network congestion or verification processes.
- The Solution: Plan ahead for potential delays. Always check the estimated processing time on the crypto platform and allow some buffer time for your transactions.
Challenge 2: High Fees
- The Issue: Some platforms charge high fees for transactions or currency conversions.
- The Solution: Compare different platforms to find the most cost-effective option. Consider the total cost, including withdrawal and conversion fees.
Challenge 3: Security Concerns
- The Issue: There are risks associated with online transactions, including hacking and phishing attacks.
- The Solution: Use platforms with robust security measures. Enable two-factor authentication and be vigilant about online security practices.
Challenge 4: Best Practices for a Smooth Transfer
- Always keep your software updated.
- Use strong, unique passwords for your accounts.
- Keep a record of your transactions for future reference and tax purposes.
Crypto to bank transfers: Legal and Tax Considerations
Navigating the legal and tax implications of transferring cryptocurrencies to a bank account is crucial for staying compliant and avoiding potential issues. This section covers key points to consider:
Understanding Legal Frameworks
- Regional Variations: Cryptocurrency regulations can vary significantly from one region to another. It's essential to be aware of the legal stance of your country or region on cryptocurrency transactions.
- Compliance: Ensure that the crypto platform you use complies with local laws and regulations. This includes adhering to anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) policies.
Tax Implications
- Reporting Obligations: In many jurisdictions, profits from cryptocurrency transactions are subject to taxes. This can include capital gains tax.
- Accurate Records: Keep detailed records of your transactions, including dates, amounts, and the value of your crypto at the time of the transaction. This information will be crucial for accurate tax reporting.
Seeking Professional Advice
- Consult Experts: Given the complexity of tax laws regarding cryptocurrencies, consider consulting a tax professional who is knowledgeable in this area. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific situation.
By staying informed about the legal and tax aspects of crypto transactions, you can ensure a compliant and hassle-free experience when transferring your digital assets to a traditional bank account.
Conclusion
Transferring cryptocurrency to a bank account is a process that bridges the innovative world of digital currencies with the more traditional realm of banking. As cryptocurrencies continue to integrate into mainstream finance, understanding how to safely and effectively carry out these transfers becomes increasingly important.
We have explored the key steps involved in this process, from selecting a reputable and secure crypto platform to understanding the nuances of legal and tax considerations. Centralized crypto banks, like Kyrrex Crypto Bank, offer a harmonious blend of traditional banking services with the flexibility of cryptocurrency transactions, making them an excellent choice for those seeking a streamlined experience.
© 2018 - 2024 All rights reserved